Fertilizer and Microorganisms
There is a need to explain an effective method for introducing microbial activators into the soil system and understanding how they influence nutrient release, soil microbiota balance, and overall soil status.
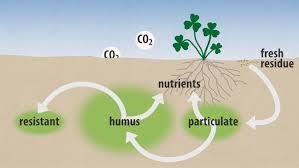
Soil fertility in the rhizosphere is influenced by plant roots and a consortium of soil microorganisms.This ultimately affects the growth, yield, composition, and nutritional quality of the produced plant biomass.Each plant shapes its surrounding environment in a unique way by affecting its chemical, physical, and biological properties.Plants stimulate soil plant and animal communities through exudates and residues after harvest, which contain various chemical compounds.Microbial metabolic by-products act as biostimulants and promote the release of nutrients that are otherwise inaccessible in the soil but can be absorbed by the plant root system.In turn, plant roots interact with microorganisms, enhancing plant growth, nutrient uptake, and protection against various biological invaders.At the same time, it has been observed that low nutrient levels in the rhizosphere can stimulate root tissues to secrete exudates, which in turn promote microbial growth.This subsequently increases the availability of previously inaccessible nutrients.Plant roots exude approximately 11 to 40 percent of the carbon fixed through their photosynthetic activity into the soil, known as root exudates.Root exudates and mucilage serve as nutrient sources and signaling molecules for soil microorganisms, altering the microbial populations around the root system.Root exudates can influence rhizosphere interactions through selective biocidal activities and/or signaling, in addition to serving as the primary carbon source for rhizosphere microbes.It has been observed that rhizosphere interactions are affected by both polar and non-polar compounds.
More complex non-polar secondary metabolites, including flavonoids, coumarins, and benzoxazinoids, along with primary polar metabolites such as organic acids and amino acids, have significant effects on rhizosphere bacteria.On the other hand, microbial mechanisms contribute to plant growth by supporting nutrient uptake, synthesizing plant growth hormones, and controlling pathogens biologically.The interactions between roots and microbial communities also affect the physical and chemical properties of the surrounding soil.Spatial and temporal dynamics influence the interaction of various rhizosphere components, resulting in dynamic feedback loops that maintain the complex rhizosphere environment with physical, chemical, and biological gradients distinct from bulk soil.
Gaining an understanding of these complex rhizosphere connections is essential for comprehending localized biogeochemical processes and developing strategies to enhance plant performance.These complex relationships are governed by the prevailing physicochemical conditions of the soil, plant type, and biodiversity of the soil flora.Each of the aforementioned components is often considered independently from the others.Therefore, the soil system should be regarded as an integration of these three components to achieve system balance and fully understand the essential interrelations.Soil fauna are frequently overlooked in the context of sustainable agricultural development.However, it has been demonstrated how soil fauna activity contributes to soil fertility.
When attempting to explain how microbial activity may promote plant growth, three mechanisms are generally cited:
(1) Modulation of plant hormone signaling;
(2) Prevention or competition with pathogenic microbial strains;
(3) Enhancement of the bioavailability of soil nutrients.
Biological Waste as a Nutrient Source
Biofertilizers are widely used in organic agricultural systems. However, there is still limited information regarding the mechanisms of this process, particularly in real agricultural environments. For example, how do plant cultivar selection, the type of “waste,” microbial inoculations, and sustainable introduction methods of biofertilizers into the soil system affect the efficacy of the process? All proposed waste compounds can undergo microbiological treatment using biofertilizers. Consequently, there is potential for the release of nutrients and biostimulants from the waste matrix. Individual cases are well documented in the literature, highlighting microorganisms and their effectiveness. However, in most cases, these are descriptive reports of laboratory experiments utilizing single strains and one type of waste [8,15]. In this context, rigorous research is necessary, including screening microbial systems that effectively degrade waste in natural systems, alongside variations in Methods of Microorganism Introduction
For instance, research on keratinases and the laboratory degradation of feathers demonstrated that keratin is not degraded solely by keratinase enzymes. The activity of keratinases is insufficient to break disulfide bonds. Subsequent processes—sulfitolysis, proteolysis, and deamination—have been identified as potential factors in keratin degradation, and numerous methods have been proposed. To understand the mechanism of keratinase action, further investigations into keratin degradation are essential. The use of multiple strains simultaneously may be an effective strategy for feather degradation. In microbial degradation contexts, it has been observed that microbial consortia or mixed microorganisms exhibit distinct effects compared to individual microbes. A comparable approach may be applied to select suitable consortia that efficiently decompose waste biomass.
Nutrient-Rich Formulations from Biological Waste
The current necessity to enhance crop productivity, soil fertility, and pest control in sustainable agriculture calls for the use of biological resources to reduce the application of chemically-based products and their associated detrimental environmental impacts. Wastes such as spent coffee grounds, spent mushroom substrate, rice husk straw, blood meal, biochar, and other significant biological wastes have been recognized as crucial for plant metabolic pathways, increasing microbial interactions, enhancing host resistance, and simultaneously inhibiting pathogen colonization. These features support the potential use of nutrient-rich formulations as effective biofertilizers and biopesticides.
The term “soil biofertilizer” refers to microorganisms that enrich the soil with nutrients and carbon substrates, including bacteria, fungi, algae, and cyanobacteria. The most common and widely used biofertilizers are green manures, which include cyanobacterial supplements and bacterial bioformulations such as Azotobacter spp., Azospirillum spp., Trichoderma spp., and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF). Farmers typically utilize organic fertilizers such as plant residues, vermicompost residues, animal manure, and other waste substrates alongside microbial biofertilizers. Solid-state fermentation has been employed to produce a biofertilizer, which was subsequently applied in vegetable gardens. The physical properties of plant samples treated with biofertilizers were positively confirmed by experimental results. Two principal methods that exploit the metabolic potential of thermophilic and decomposer bacterial populations are composting and anaerobic digestion (AD). Indigenous microbial communities possess enzymes that support biological processes converting agricultural waste into biofertilizers.
Microorganisms
The implementation of sustainable agricultural assumptions within the European Union requires increased attention to the beneficial effects of biostimulants, which by definition do not supply nutrients themselves but enable improved crop parameters while significantly reducing chemical fertilizer use. Although the term “biostimulant” has become a permanent feature of scientific and professional literature, it was first used only in 2007. Previously, terms such as substances that enhance plant growth in small amounts, “hormone-containing products,” or metabolic enhancers were employed. Nevertheless, over the years, the term “biostimulant” has been increasingly utilized in scientific publications, encompassing a broader range of compounds and modes of action.
Currently, biostimulants are classified into five categories:
- Seaweed and plant extracts;
- Humic substances;
- Hydrolyzed proteins and nitrogen-containing compounds;
- Microorganisms;
- Mineral compounds with biostimulant activity.
Their increasing importance in agricultural practice is primarily based on their highly favorable properties, which relate not only to product quality and improved performance under stress conditions but also to reducing negative impacts on the natural environment. By reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, they have contributed to changes in fertilization regulations.
Biostimulants are included in the new Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and Council, published on June 5, 2019. This regulation also distinguishes between microorganisms and their exclusion from certain regulatory frameworks. Currently, the following goods fall under the EU Fertilizer Products Regulation framework: 1. fertilizers; 2. liming materials; 3. soil improvers; 4. growing media; 5. inhibitors; 6. plant biostimulants, including (a) microbial plant biostimulants and (b) non-microbial plant biostimulants; and 7.fertilizer product mixtures.
According to the aforementioned EU legislation, a plant biostimulant is defined as any substance that enhances the plant nutrition process irrespective of its nutrient content, with the explicit aim of improving one or more of the following characteristics of the plant or its rhizosphere:
(1) nutrient use efficiency; (2) tolerance to abiotic stress; (3) quality traits; (4) availability of confined nutrients in the soil or rhizosphere. In other words, this group consists of products that enhance plant growth but do not supply nutrients themselves. Biostimulants support natural processes within plant tissues due to the presence of substances such as beneficial soil microorganisms and phytohormones like auxins, cytokinins, or amino acids. Within this category of compounds/materials, a group of products known as biofertilizers is recognized.
Microbial biofertilizers consist of beneficial microbial cells that interact with the rhizosphere or endosphere of plants and promote plant growth. They utilize elements already present in the soil to supply substances that stimulate plant growth. By encouraging nutrient uptake and ultimately increasing productivity, they enhance soil fertility. Numerous commercial products formulated with selected soil microorganisms primarily aim to increase nutrient availability. Furthermore, some preparations contain biostimulants that enhance resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses, although they do not supply nutrients themselves.
Review of Various Microbial Formulations
Microbial Formulation Technology
A major challenge in soil ecology is the diverse and dynamic soil microbial population, which varies between compartments and layers. The potential environmental effects of inoculation have never been a primary concern. Inoculation causes at least a temporary disruption of the soil microbial community balance by providing a high density of effective and viable microorganisms for rapid colonization of the host rhizosphere.
If important native species disappear, it may negatively affect future yields by altering the microbiota and causing undesirable changes. However, the degree of diversity and interactions between the plant, soil, and microbiota may act as a buffer against inoculation-induced changes in microbial population structure. Since several bacterial species may perform similar functions, bacterial redundancy may prevent loss of specific species from impairing system function. Microbial formulations are suitable alternatives to chemical inputs because microbial inoculants are ecologically benign or “environmentally friendly.” They can function as microbial biocontrol agents, biofertilizers, or plant stimulants. Bioherbicides can also be produced from natural bacteria isolated from their native environment and sprayed on plants. Relatively large quantities of microbial cells are introduced into the competitive soil environment to utilize microbial inoculants. Various types of microorganisms have been investigated and are frequently used as microbial antagonists. The discovery of new species, selection and enhancement of established strains, and introduction of non-native genes to obtain expressed products or novel functional traits have all contributed to recent advances in classical microbiology. We refer to this complex and beneficial branch of microbiology as technological advancements in microbiology.
Various organic and mineral carriers are used in the formation of microbial isolates employing liquid or solid formulation techniques. These are applied via soil and foliar spraying, seed treatment, bio-priming, seedling dipping, or a combination of strains as inoculants or consortia.
Single Inoculations
Today, a wide range of single microorganisms are commercially available as microbial inoculants. Several entomopathogenic fungi are also used as control agents, including Beauveria, Metarhizium, Verticillium, and Paecilomyces. These fungi are mainly applied in greenhouses and other relatively humid environments to control leafworms. Multiple arthropod species are susceptible to the effects of Beauveria bassiana. When fungal spore preparations are used, the efficacy of fungal microbiological treatments is significantly influenced by environmental parameters such as temperature and humidity. However, infection establishment may cause insect mortality long before chemical controls are applied. Both non-target effects and the potential for resistance development are considerably reduced. Spores commonly adhere to insect cuticles, germinate, and penetrate upon contact. Naturally, a broad spectrum of toxins and molecules that induce behavioral changes or modifications are released by various entomopathogenic fungi (Cordycipitales, Trichocomaceae, etc.). Several lepidopteran insect larvae have been effectively controlled by fungi.
C.F. Von Tubeuf was the first to introduce the term “biological control” as a practical aspect in plant disease management in 1914. Since then, it has been discovered that various biocontrol agents are highly successful in plant disease management. Sanford found that the antagonistic activities of green manure inhibit potato scab. Weindling demonstrated that Trichoderma lignorum is a parasite of several plant diseases. Grosbard, Wright, and others showed that Penicillium, Aspergillus, Trichoderma, and Streptomyces species produce antibiotics in soil. Clouper highlighted the importance of siderophores produced by Erwinia carotovora. Howell reported strains P and Q of Trichoderma sp. The chlamydospore suspension of Phytophthora palmivora was the first registered commercial herbicide used to control Morrenia odorata.
Several microorganisms such as Trichoderma harzianum, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Bacillus subtilis can control many foliar and soil-borne fungi, for example Fusarium spp., Rhizoctonia solani, Pythium spp., Rolfssi, and Sclerotium in vegetables and industrial products. The goal of Trichoderma is to produce mycoparasitic strains effective in controlling fungal plant diseases in various environments. It was found that some Bacillus species penetrate root surfaces, promote plant growth, and induce lysis of fungal mycelia. Since B. subtilis cells can produce dormant spores resistant to harsh environments, their preparation and storage are simple. Moreover, B. subtilis produces a wide range of physiologically active substances exhibiting diverse activities against plant pathogens and the ability to induce systemic resistance in hosts. It has also been shown that several B. subtilis strains can form multicellular structures or biofilms. These advantageous traits make B. subtilis a promising candidate for use as a biocontrol agent. Reports indicate that specific strains of B. subtilis can successfully control wilt diseases caused by Ralstonia species in various plant hosts .In agricultural environments, bacteria, mycorrhizae, and other fungi may all contribute to growth promotion while providing biocontrol. These organisms may act as biocontrol agents, minimize pathogen damage to plants, or alter levels of vital plant hormones such as auxin and ethylene. They may also assist plants in acquiring essential resources like iron, phosphate, nitrogen, or water. Genera such as Rhizobium, Sinorhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Azorhizobium, and Allorhizobium include some of the most effective nitrogen-fixing strains. Pochonia chlamydosporia and P. fluorescens effectively control nematode-induced diseases. Significant advances in the development and distribution of bionematicides have been made in recent years. Avermectins—secondary metabolites of the bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis—serve as model pesticides, as they are effective against nematodes even at very low doses and are non-toxic to mammals. Thus, nematodes and adult larvae such as Radopholus similis, Meloidogyne incognita, and Ditylenchus dipsaci become immobilized and die upon exposure to filtrates from Bacillus firmus cultures, indicating that toxic compound production plays a role in pest management.
Co-inoculation
Reported variations in this field may be partly explained by the fact that inoculations often rely on the application of a single strain. Adding multiple beneficial microbial species or strains to a microbial consortium is a method to overcome this limitation. Without the need for genetic engineering, co-inoculation combines many approaches to improve plant performance and the efficacy and reliability of beneficial effects on crops. To enhance plant production, physiological parameters, and regulate plant health, co-inoculation of biocontrol agents and biofertilizers is considered a beneficial strategy. Through various modes of action, the use of distinct microbes can broaden the scope of biocontrol activity, improve efficacy and reliability in disease suppression, and promote plant growth without genetic engineering techniques.
Soil contains an unlimited number of microbes, including harmful organisms. Isolating and evaluating several beneficial microbes with different modes of action for biocontrol and plant growth promotion is an emerging research area. Introducing beneficial microbes isolated from the soil ecosystem reflects the natural state and can replace harmful microbes when applied at higher inoculation levels. Additionally, the use of mixtures of beneficial microbial cultures increases the efficiency and reliability of plant health management. However, specific microbial strain mixtures may negatively impact pathogen infection suppression and plant growth promotion [78]. Furthermore, inoculations composed of many arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi can be produced. For instance, the AM fungus Funneliformis mosseae has been shown to systematically reduce disease infection in barley caused by Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici. Thygesen et al. discovered potential mycorrhiza-induced resistance against the pathogen Aphanomyces euteiches causing pea root rot. Moreover, differences in tolerance induction levels were observed between two AM fungi, Glomus claroideum and G. intraradices. Abdelfattah et al. reported that both greenhouse and field treatments with a combination of AM fungi (Glomus intraradices, G. mosseae, G. clarum, Gigaspora margarita, and G. gigantea) effectively reduced white root rot disease in onions caused by Sclerotium cepivorum.
Microbial Consortium
Since bacteria do not exist in isolation in natural environments, groups of bacteria may be more beneficial for promoting plant growth than a single bacterium. However, developing bacterial consortia and their composition is challenging because the mixed bacterial members must be compatible with each other. Bacteria selected for a consortium should be adapted to the adverse conditions of agricultural fields and possess diverse capabilities for promoting plant growth and bioremediation. There is a higher likelihood that a bacterium within a consortium expresses the functional genes necessary for plant growth promotion, which is another important reason why bacterial consortia may perform better than single-bacterium formulations.
Several studies have demonstrated that a single strain cannot completely degrade pollutants. Since different strains have diverse metabolic pathways, bacteria with varying reduction capabilities can be combined, and a microbial consortium may integrate the advantages of each strain to ensure effective pollutant degradation. Mixed microbial consortia have shown high performance in substrate tolerance and enhanced pollutant degradation. Microbial consortia outperform single-strain cultures. Microbial consortia have exhibited clear effects on pollutant degradation. Some relevant microbial strains isolated from gut and natural flora possess inherent potential for pollutant degradation. Lactobacilli, actinobacteria, Pseudomonas, Clostridium, Salmonella, and E. coli have been identified as having intrinsic pollutant degradation abilities. These strains are suitable for bioremediation. Microbial consortia have become vital tools as they reduce pollutants more effectively than single strains. Bioremediation is often performed by microbial consortia rather than individual species in natural environments, where different species carry out separate functional tasks. Co-culturing microbial consortia is more effective than single bacteria, degrading pollutants faster and potentially significantly increasing bioremediation in soil.
From both economic and environmental perspectives, sterilizing biomass waste is impractical. Therefore, applied science research on synthetic microbial consortia (SMC) should focus on non-sterile conditions. However, the indigenous microbial structure in biomass waste is complex and variable, especially in continuous or semi-continuous processing where continuous substrate addition significantly influences the existing microbial community structure. This requires higher robustness and resilience of SMC against disturbances. Immobilization methods may reduce or eliminate this problem. Furthermore, commercialization, which offers significant advantages in maintaining microbial activity during storage and transportation of SMC, also depends on immobilization.
Soil Application
When biocontrol agents (BCAs) are vulnerable to excessive desiccation, commonly occurring during drought and hot weather, soil treatment is recommended. BCAs control disease by establishing a strong population in the soil. In these situations, niche exclusion is also relevant, as increasing the amount of newly introduced microorganisms prevents soil pathogens and other low-benefit microflora from accessing vital nutrients. Both beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms are stored in the soil, and the addition of microbial inoculants to soil enhances the dynamics of antagonistic bacterial populations and prevents the spread of pathogenic microbes to infection sites. Several Trichoderma species have been extensively synthesized using carriers and cellulose-based adhesives, as well as contemporary thin-layer coating methods, and introduced into the rhizosphere zones of seedlings to protect against soil-borne diseases including Pythium ultimum and Rhizoctonia solani. However, the initial limitation of fungi as seed coatings persists. Thus, fungi are less capable of penetrating the rhizosphere compared to bacterial agents. Several attempts have been made to introduce naturally colonized substrates by pathogen antagonists into the soil to manage a number of soil-borne diseases. Despite the use of aqueous dispersions of biocontrol agents for soil inoculation, distribution of biocontrol agents in soil may be uneven. Bankoul and Adbanjo concluded that soil inoculation with Trichoderma viride significantly reduced infection levels in cowpea seeds contaminated by Colletotrichum truncatum (brown spot). Application of Trichoderma harzianum in soil effectively controlled peanut stem rot caused by Sclerotium rolfsii. Chrysanthemum wilt was suppressed by an aqueous dip containing T. harzianum conidia which prevented re-infection by Fusarium oxysporum. Weststeijn discovered that soil inoculation with Pseudomonas suspension at a concentration of 10^8 cells per gram of dry soil before planting onion reduced root rot caused by Pythium ultimum in tulip trees. Use of the Pseudomonas strain N24 on seedbeds at 500 ml per square meter in greenhouses decreased wilt disease in sunflower.
Challenges and Limitations in Microbial Formulation Technology
Limitations and challenges in microbial formulation technology utilizing the potential of beneficial soil microorganisms to produce biofertilizers that improve plant performance have gained attention in recent years. Although this strategy has achieved many successes, it is not without problems and limitations. One of the main barriers is the difficulty in reproducing their beneficial effects on plants in field conditions under constantly changing environmental parameters. Furthermore, agricultural communities need greater awareness of the ecological significance of these microbial formulations and the scientific methods for their use in this field. Educational and awareness initiatives are essential to enhance acceptance and effective implementation. Ethical concerns may also arise, especially if genetically modified microbes or non-native species are used in these formulations. Acceptance of such techniques may be significantly influenced by societal approval. Additionally, the existing natural soil microbial populations may pose substantial obstacles to the effective application of these inoculants. It is uncertain whether microbial biofertilizers perform consistently across various crop types and conditions. Efficient selection of the most effective microbial strains for a given agricultural environment may be challenging. Moreover, other parameters, including soil type, temperature, pH, and moisture content, may influence the efficacy of these strains. Short shelf life of microbial preparations is another drawback. Microbes in these formulations may become less viable over time, potentially reducing their field effectiveness. Rigorous quality control during production is essential to maintain product uniformity and efficacy. Studies on commercial biofertilizers have revealed problems related to contamination and the presence of unwanted bacterial strains. For instance, Herman and Lesueur analyzed 65 commercial biofertilizers and found that only 37% met the criteria for labeling as “pure.” Conversely, 63% of evaluated biofertilizers showed contamination signs from one or more bacterial species. Furthermore, 40% of tested items contained impurities and lacked fully identified strains. Other limitations include the lack of suitable carriers for these formulations, poor storage facilities preventing contamination, and unpredictable efficacy due to harsh weather conditions. Absence of important labeling information such as expiration dates and microbial identities used in production may undermine confidence in biofertilizers. Selectivity in most biofertilizer processes limits their compatibility with specific pesticides or chemical fertilizers and potentially impacts integrated pest management or nutrient management programs. Overcoming these barriers and limitations requires collaboration among scientists, agricultural professionals, and policymakers, with continuous research and development. To promote sustainable agricultural practices, it is essential to evaluate and invest in the potential benefits of microbial formulations while actively addressing their drawbacks.